Knee replacement alternatives
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, involves replacing a knee joint with a prosthetic device. Explore the alternatives to this procedure and their benefits.
Why Consider Knee Replacement Alternatives?
Many patients seek alternatives due to persistent pain and potential risks associated with knee replacement surgery.
Challenges of Knee Replacement
Patients often experience continued pain post-surgery, with studies showing significant discomfort even years later.
Common Risks of Knee Replacement
Understand the risks involved, including increased susceptibility to cardiovascular events and allergic reactions to prosthetic materials.
Types of Knee Replacement Alternatives
Discover effective alternatives that offer relief without the complexities of surgery.
Steroid Injections
While providing short-term relief, steroid injections may not offer long-term solutions due to their impact on cartilage.
Viscosupplementation
Gel-like substances such as hyaluronic acid injections offer relief for knee arthritis, though effectiveness may vary over multiple doses.
Knee Nerve Ablation
A promising procedure that involves disabling nerves around the knee joint to alleviate pain, though long-term outcomes are still under study.
Orthobiologics
Utilizing natural substances like PRP and BMC to promote healing and reduce degradation of knee tissues, offering both autologous and allogeneic options.
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
Derived from the patient’s blood, PRP injections foster cartilage repair and reduce inflammation, beneficial for moderate knee arthritis.
Percutaneous Knee Arthroplasty (PKA)
A sophisticated procedure involving precise injections of bone marrow concentrates guided by ultrasound, effective even in severe cases of knee arthritis.
- Published in Blog
What Are The Best Options For Managing Chronic Pain?
Chronic pain is a debilitating condition affecting millions worldwide. Explore effective strategies and treatments to alleviate persistent discomfort.
Understanding Chronic Pain Causes
Learn about the underlying factors contributing to chronic pain, from inflammation triggered by injuries to environmental and physiological influences.
Common Chronic Pain Conditions
Discover prevalent conditions like osteoarthritis, migraine, multiple sclerosis, neuropathy, and fibromyalgia, each posing unique challenges and symptoms.
Impact of Chronic Pain
Understand the profound impact of chronic pain on daily life, including physical limitations, emotional distress, and the risk of opioid dependency.
Management Strategies for Chronic Pain
Explore various treatment approaches recommended by healthcare professionals to manage chronic pain effectively.
Analgesics
Overview of commonly used pain relievers such as NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and aspirin, along with considerations for long-term use and potential side effects.
Anticonvulsants
Explore how anticonvulsant medications like Gabapentin and Lyrica are repurposed to manage chronic pain, highlighting their effectiveness and side effects.
Antidepressants
Learn about the role of antidepressants in treating chronic pain, including tricyclics and SNRIs, and their dual impact on pain relief and mood stabilization.
Opioids
Discussion on the use of opioids for severe chronic pain, emphasizing careful management due to addiction risks and monitoring protocols.
Alternative Medicine
Explore natural remedies and alternative therapies like herbal treatments and cannabinoids, gaining popularity as complementary approaches to pain management.
Could Stem Cell Regeneration (SCR) Be the Solution?
Investigate the potential of stem cell therapy in chronic pain management, including types of stem cell treatments, their benefits, and current research insights.
Types of Stem Cell Therapy
Differentiate between autologous and non-autologous stem cell therapies, highlighting their sources, applications, and potential outcomes.
Research and Effectiveness
Review current studies and findings on mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy, assessing its efficacy in treating conditions like osteoarthritis and neuropathic pain.
Considerations and Risks
Understand the risks associated with stem cell therapy, including tumor formation and immune reactions, balanced against its promising results in pain reduction.
- Published in Blog
MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS
Over the past decade, cellular therapy has rapidly advanced in both preclinical and clinical settings. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have garnered significant interest in regenerative medicine due to their unique biological properties.
Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cells are multipotent stromal cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, myocytes, and adipocytes. They play crucial roles in tissue repair, wound healing, and cell substitution.
Sources of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Initially isolated from bone marrow, MSCs can now be sourced from various tissues such as adipose tissue, dental pulp, umbilical cord, and placenta. Each source offers unique advantages in terms of accessibility and therapeutic potential.
History and Development
The concept of MSCs dates back to the late 19th century with Cohnheim’s hypothesis on fibroblastic cells in wound healing. Alexander Friedenstein’s work in the 1970s further characterized MSCs, demonstrating their colony-forming ability and osteogenic differentiation potential.
Clinical Applications
MSCs have been extensively studied and applied in treating immune-based disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes, as well as orthopedic conditions such as osteoarthritis and spinal cord injuries. Their immunomodulatory properties make them promising candidates for gene therapy and insulin production.
Current Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research focuses on enhancing MSC therapy efficacy, addressing challenges like tumor formation and immune reactions. Advancements in culturing techniques and understanding MSC behavior in vivo are critical for expanding their clinical applications.
Conclusion
Mesenchymal stem cells represent a pivotal frontier in regenerative medicine, offering new avenues for treating chronic diseases and injuries. Continued research is essential to fully harness their therapeutic potential.
REFERENCES
- Wei X, Yang X, Han ZP, Qu FF, Shao L, Shi YF. Mesenchymal stem cells: a new trend for cell therapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Jun; 34(6):747-54
- Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky II S, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966;16:381–90
- Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Latsinik NV, Panasyuk AF, Keiliss-Borok IV. Stromal cells responsible for transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues. Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation. 1974;17:331–40.
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–7.
- Caplan AI, Dennis JE. Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98:1076–84.
- Wang S, Qu X, Zhao RC. Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells. Journal ofHematology & Oncology. Apr 30, 2012;5:19.
- Dominici, M., Le Blanc, K., Mueller, I., Slaper-Cortenbach, I., Marini, F., Krause, D., Deans, R., Keating, A., Prockop, D. and Horwitz, E. (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular. Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8, 315–31.
- Published in Blog
Which are the best options For Treating Common Sports Injuries?
As physicians, dealing with sports injuries is a routine challenge. While not usually life-threatening, these injuries can lead to long-term issues if not managed properly. They range from ankle sprains to ACL tears and tennis elbow, affecting athletes’ performance and quality of life.
What Are the Most Common Sports Injuries?
Sports injuries vary widely but often include:
Ankle Sprain
Ankle sprains result from ligament stretching or tearing due to sudden twisting or falls. Without proper treatment, they can lead to chronic pain and instability.
Groin Pull
Common among athletes requiring quick movements, groin pulls involve muscle tears in the inner thigh/groin area, causing tenderness and bruising.
Hamstring Strain
Overstretching the hamstring muscles can lead to tears, requiring months to heal and prone to re-injury without proper care.
Shin Splints
Inflammation of leg muscles from repetitive stress, common in runners and athletes with intense stop-and-go motions.
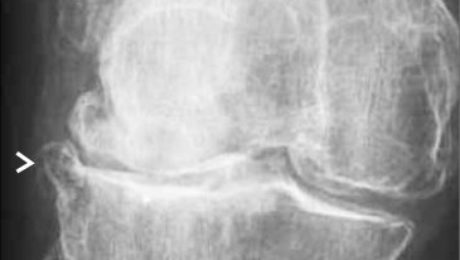
Knee Injury: ACL Tear
A torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is common in sports requiring sudden stops or direction changes, causing instability and swelling.
Knee Injury: Patellofemoral Syndrome
Damage to knee cap tissues from repetitive movements, often due to muscle weakness or alignment issues.
Tennis Elbow (Epicondylitis)
Ligament strain from repetitive wrist and hand motions, common in sports like tennis or golf.
Traditional Treatment Options & Management Strategies
For mild injuries, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) along with NSAIDs are recommended. Moderate to severe injuries may require immobilization, rehabilitation exercises, or even surgery for ligament or muscle repair.
Is Stem Cell Therapy An Option For Treating Sports Injuries?
Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity for its ability to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and enhance recovery in sports injuries. It’s particularly effective for tendon, ligament, muscle, and cartilage damage. While debated, it has shown promising results in improving joint function and reducing pain.
- Published in Blog
How To Effectively Treat Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Although a rare neurologic condition, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is the most common type of Motor Neuron Disease (MND), affecting voluntary muscles. This progressive disorder leads to muscle weakness and atrophy due to nerve dysfunction.
Types of ALS
ALS has two types:
- Sporadic ALS: This common type occurs without a clear cause.
- Familial ALS (FALS): Genetic and runs in families due to abnormal gene changes.
Symptoms of ALS
Symptoms include muscle weakness, progressive muscle wasting, difficulty in motor activities, and more.
Causes of ALS
While the exact cause is unknown, genetic changes and environmental factors play roles.
Diagnosis of ALS
Diagnosis involves tests like Electromyography (EMG), Nerve Conduction Study (NCS), and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Treatment Options for ALS
Management includes multidisciplinary support, medication like Riluzole and Edaravone, lifestyle adjustments, speech therapy, dietary plans, and breathing support.
Is Stem Cell Therapy an Option?
Research into Stem Cell Therapy shows promise in delaying disease progression and enhancing motor neuron recovery, though further studies are needed.
- Published in Blog
The Keto Diet: A Miracle Formula Or A Dangerous Risk?
Introduction to the Keto Diet
We live in a world overloaded with diets and eating plans that are all preaching miracle, long term results for weight loss and reducing risks of developing illnesses and diseases.
What is a Keto Diet?
To put it simply, a ‘keto’ or ‘ketogenic’ diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that puts the body into a metabolic state called ketosis.
Benefits of the Keto Diet
Weight Loss & Appetite Suppression
The biggest benefit of the keto diet and the one most dieters are striving for is weight loss and suppression of appetite.
Diabetes Type 2 Management
A keto diet can help manage diabetes type 2 by controlling glucose levels through reduced carbohydrate intake.
Epilepsy Treatment
Since the 1920s, the keto diet has been used to treat epilepsy, showing significant reduction in seizures for many patients.
Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia Prevention
Studies suggest that a ketogenic diet may help protect against Alzheimer’s disease and dementia by improving neurovascular function.
IBS & Digestive Health
For those suffering from IBS and other gastrointestinal conditions, a keto diet can lead to significant improvements by reducing carbohydrate intake.
Risks of the Keto Diet
Medical professionals have identified risks associated with the keto diet, including:
- Nutrient deficiencies (selenium, magnesium, vitamins B and C)
- Potential liver and kidney problems
- Constipation and other digestive issues
- “Keto Flu” symptoms due to carbohydrate deprivation
Conclusion
Medical opinions on the keto diet vary. While it offers promising benefits, it also poses risks that should be carefully considered.
Share Your Experience
Have you recommended the keto diet to your patients? What are your thoughts on its benefits and risks?
Final Thoughts
Discussing the potential benefits and risks of the keto diet can help patients make informed decisions about their dietary choices.
These headings help structure the content for better SEO and readability while addressing key points about the keto diet.
- Published in Blog
James P. Allison, PhD. Nobel Prize in Medicine
To improve the on-page SEO for the article on James P. Allison and his work in immunotherapy, here are suggested H2 headings and optimizations:
Introduction to James P. Allison, PhD
James P. Allison, Chair of the Department of Immunology and Director of the Immunotherapy Platform at MD Anderson Cancer Center, has dedicated his career to revolutionizing cancer treatment.
Early Influences and Motivations
Losing his mother to lymphoma and two uncles to melanoma and lung cancer deeply influenced Allison’s decision to pursue cancer research.
Focus on T Cells and Immunotherapy
Allison’s interest in T cells, pivotal warriors of the immune system, sparked during his undergraduate studies at the University of Texas at Austin.
Development of Checkpoint Blockade Antibodies
Allison’s breakthrough involved preventing immune “brakes” from engaging, allowing T cells to continue attacking and eliminating tumors.
Impact of Ipilimumab (Yervoy) on Melanoma Treatment
Ipilimumab, developed by Allison’s team, significantly extended survival rates for patients with metastatic melanoma.
Advancements in PD-1 Blockade Therapy
Further developments in PD-1 blockade therapies have expanded treatment options for various cancers including head and neck, lung, kidney, and bladder cancers.
Future Directions in Immunotherapy Research
Allison’s lab continues to explore combinations of checkpoint blockades to optimize treatment responses across different cancer types.
Integration of Immunotherapy with Traditional Treatments
While not replacing traditional therapies, Allison believes immunotherapy will become integral to comprehensive cancer treatment strategies.
Conclusion: The Future of Immunotherapy
James P. Allison’s contributions have transformed cancer care, offering hope for longer and improved quality of life for cancer patients worldwide.
Share Your Insights
What are your thoughts on the impact of immunotherapy in cancer treatment? Share your experiences and opinions.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the pioneering work of James P. Allison sheds light on the transformative potential of immunotherapy in oncology.
These headings help organize the content for better SEO and readability, highlighting key aspects of James P. Allison’s career and his contributions to cancer research and immunotherapy.
- Published in Blog
Opioid Overdose Crisis in America.
Introduction to the Opioid Overdose Crisis
America is facing a profound opioid crisis, overshadowing other public health issues with devastating consequences.
Scope and Impact of the Crisis
The opioid crisis claims an average of 130 lives daily in the United States, drastically reducing life expectancy.
Causes and Contributors
Explore the factors contributing to opioid addiction, including over-prescription of pain relievers and the rise of synthetic opioids.
Economic and Health Burden
The economic burden of opioid misuse in the US is estimated at $78.5 billion annually, encompassing healthcare costs, lost productivity, and more.
Facts and Statistics
Rise in Prescription Rates
Opioid prescriptions surged from 112 million to 282 million between 1992 and 2012, declining slightly to 236 million by 2017.
Impact on Overdose Deaths
About 68% of the 70,200 drug overdose deaths in 2017 were opioid-related, a stark increase from previous decades.
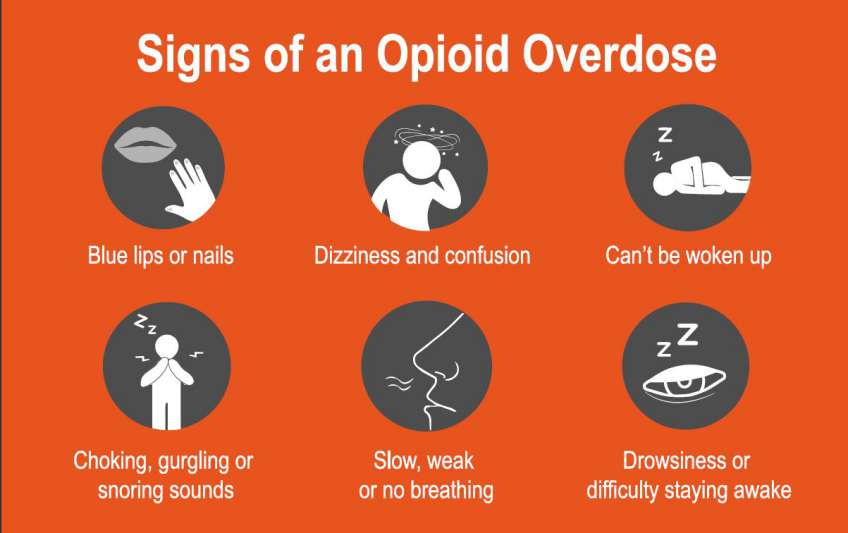
Misuse and Addiction Rates
Studies show that 21-29% of patients with chronic pain misuse prescription opioids, contributing to addiction rates.
Efforts to Combat the Crisis
Government Initiatives
The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is tackling the crisis through initiatives focusing on overdose-reversing drugs, treatment access, research, public health surveillance, and pain management improvements.
HEAL Initiative
Introduced by the NIH, the HEAL (Helping to End Addiction Long-term) Initiative aims to accelerate scientific solutions to the opioid crisis.
Conclusion: Moving Forward
Despite media attention deficits, the opioid crisis demands urgent attention and coordinated efforts to mitigate its devastating impact on American communities.
Share Your Insights
What are your thoughts on the opioid crisis and its management strategies? Share your perspectives and experiences.
Final Thoughts
Addressing the opioid overdose crisis requires continued collaboration and innovation across healthcare, research, and public policy domains.
These headings structure the content for better SEO and readability, focusing on key aspects of the opioid overdose crisis and efforts to address it in the United States.
- Published in Blog
Autologous mesenchymal stem cell application for cartilage defect in recurrent patellar dislocation: A case report
Introduction
Recurrent patellar dislocation is characterized by repeated episodes of knee cap displacement, often resulting in cartilage lesions and chronic symptoms. Traditional management approaches often yield limited success, necessitating innovative treatments such as mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy.
Case Presentation
Patient History and Examination
A 21-year-old male presented with left knee discomfort following recurrent patellar dislocations over ten years. Physical examination revealed anterior knee pain exacerbated by activities like stair climbing and exercise. Diagnostic imaging confirmed significant cartilage defects, classified as Grade 3 according to ICRS standards.

Surgical Intervention
The patient underwent arthroscopic microfracture and autologous bone marrow-derived MSCs implantation following Fulkerson osteotomy. Surgical procedures included lateral retinaculum release and tibial tubercle realignment to stabilize the patella.


Treatment Outcome
Postoperative Recovery
Post-surgery, the patient achieved full range of motion and began weight-bearing exercises. Eighteen months later, MSC implantation facilitated significant cartilage growth, improving International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) and Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores.
Long-term Assessment
Two years post-MSC treatment, the patient reported no knee complaints and maintained full range of motion. MRI confirmed substantial cartilage regeneration in previously damaged areas.

Discussion
Challenges in Management
Recurrent patellar dislocations pose challenges due to high recurrence rates and associated cartilage damage. Treatment strategies like Fulkerson osteotomy combined with MSC therapy offer promising outcomes for severe cases.
Role of MSC Therapy
MSCs demonstrate potential in cartilage regeneration due to their chondrogenic differentiation capabilities and anti-inflammatory properties. This case highlights the efficacy of MSC therapy in managing extensive cartilage defects.
Conclusion
Combining Fulkerson osteotomy with MSC implantation represents a viable treatment option for chronic patellar instability and associated cartilage lesions. The integration of microfracture and MSC therapy supports significant cartilage regeneration and functional recovery.
- Published in Blog
Autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue for the treatment of diffuse degenerative knee osteoarthritis: an update at 3 year follow-up
Background
The management of chondral disease poses challenges due to its poor healing potential. Biomechanical and biological changes can accelerate degeneration, leading to end-stage osteoarthritis (OA).
Conservative Therapies
Various conservative treatments are utilized before surgery, including non-pharmacological interventions and intra-articular therapies. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), particularly from adipose tissue, show promise in cartilage regeneration due to their anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties.
Methods
The study, approved by the Ethics Committee, involved 30 patients with diffuse degenerative chondral lesions treated with autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue between January and December 2014. Clinical evaluations were conducted at 3 years post-treatment.
Findings
Of the 30 patients, 24 underwent associated surgeries, while 6 had arthroscopy alone. At 3 years, 23% of patients received additional treatments. No adverse events were reported.
Results
Patients not requiring additional treatments maintained outcomes observed at 1 year, with significant improvements in functional scores including Tegner Lysholm Knee, VAS pain, IKDC subjective, and total KOOS.
Discussion
The study demonstrates sustained benefits of autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue in treating diffuse degenerative knee chondral lesions at mid-term follow-up, supporting its role as an adjunct in surgical procedures.
Conclusion
Micro-fragmented adipose tissue shows promise in mitigating chondral degeneration, warranting further investigation into its protective effects in knee OA management.
References.
- Ährlund-Richter L, De Luca M, Marshak DR, Munsie M, Veiga A, Rao M (2009) Isolation and production of cells suitable for human therapy: challenges ahead. Cell Stem Cell 4(1):20–26View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Arcidiacono JA, Blair JW, Benton KA (2012) US Food and Drug Administration international collaborations for cellular therapy product regulation. Stem Cell Res Ther 3(5):1View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Bonasia DE, Dettoni F, Sito G, Blonna D, Marmotti A, Bruzzone M, Castoldi F, Rossi R (2014) Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment overload/arthritis in the varus knee: prognostic factors. Am J Sports Med 42(3):690–698View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Caplan AI (2008) All MSCs are pericytes? Cell Stem Cell 3(3):229–230View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Caplan AI, Correa D (2011) The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell 9(1):11–15View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Caplan AI, Dennis JE (2006) Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J Cell Biochem 98(5):1076–1084View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- De Girolamo L, Kon E, Filardo G, Marmotti A, Soler F, Peretti G, Vannini F, Madry H, Chubinskaya S (2016) Regenerative approaches for the treatment of early OA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(6):1826–1835View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Pak J, Lee JH, Kartolo WA, Lee SH (2016) Cartilage regeneration in human with adipose tissue-derived stem cells: current status in clinical implications. Biomed Res Int 2016:4702674View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Røtterud JH, Risberg MA, Engebretsen L, Årøen A (2012) Patients with focal full-thickness cartilage lesions benefit less from ACL reconstruction at 2–5 years follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(8):1533–1539View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ruetze M, Richter W (2014) Adipose-derived stromal cells for osteoarticular repair: trophic function versus stem cell activity. Expert Rev Mol Med 16:e9View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Russo A, Condello V, Madonna V, Guerriero M, Zorzi C (2017) Autologous and micro-fragmented adipose tissue for the treatment of diffuse degenerative knee osteoarthritis. J Exp Orthop 4(1):33View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Saithna A, Kundra R, Getgood A, Spalding T (2014) Opening wedge distal femoral varus osteotomy for lateral compartment osteoarthritis in the valgus knee. Knee 21(1):172–175View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sensebé L, Bourin P, Tarte K (2010) Good manufacturing practices production of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Hum Gene Ther 22(1):19–26View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Su X, Li C, Liao W, Liu J, Zhang H, Li J, Li Z (2018) Comparison of arthroscopic and conservative treatments for knee osteoarthritis: a 5-year retrospective comparative study. Arthroscopy 34(3):652–659View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Verdonk R, Madry H, Shabshin N, Dirisamer F, Peretti GM, Pujol N, Spalding T, Verdonk P, Seil R, Condello V (2016) The role of meniscal tissue in joint protection in early osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(6):1763–1774View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Published in Blog


![services-knee-replacement[1]](https://www.issca.us/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/services-knee-replacement1-460x260_c.jpg)